What is Banking?
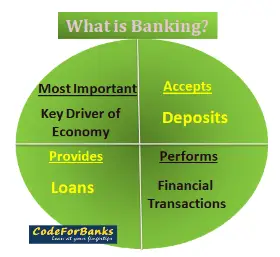
Banking is one of the most important key drivers of any economy. Banking can simply be understood as an industry that manages cash & credit and performs other financial transactions too.
In general terms, Banking is a business activity of accepting deposits by individuals & entities and then lending this money in order to earn a profit.
"Banking" has been defined in the Cambridge English Dictionary as follows:
- Banking is the business of operating a bank
- Banking is the activity of managing the money in your bank accounts
Interested to know Why you should not keep All Your Money in Banks Savings Account?
Who carries out Banking Function?
Banking Function is carried out by financial intermediaries, which perform the functions of accepting & safeguarding deposits and extending loans to the customers.
What is a Banking System?
Banking System is the prime mechanism through which the money supply of the country is created and controlled. Banking System a network of banks which accept deposits from general public and other entities, provides money transmission and offers other financial services such as loan and credit facilities to the borrowers and invests in corporate debentures and government securities.
Interest to know Become a Crorepati in the age of 40: the secret revealed
How does Banking System work?
Following are the detailed process in order to explain how does banking system work:
- Banks accept cash from its customers as deposits. Banks also pay a small percent, the interest rate, on the deposit.
- Banks then lend major portion of these deposits in the form of different loans to their borrowers.
- Banks are required to keep a small percent of such deposit on hand under a regulation, which is called the reserve requirement.
- Banks earn money by charging higher interest rates on their loans than what they pay on the deposits.
Types of Banking
There are following types of Banking:
- Retail Banking: It deals directly with Individuals and Small Business Entities
- Business Banking: It offers services to Medium Sized Businesses
- Corporate Banking: Services are focussed at Large Business Houses
- Private Banking: Wealth Management Services are provided to high-net-worth individuals (HNIs)
- Investment Banking: Services are directed towards activities on the financial markets
What is a Bank?
All the persons like individuals, businesses and even the government need somewhere to deposit and borrow money, Here banks play a major role.
Bank is one entity which transacts the business of banking. It is a licensed and regulated financial institution that, accepts deposits, lends money and carries out other financial transactions for its clients.
Banks is a safe place to deposit extra cash. Deposits can be available on demand (e.g. a current account) or with some restrictions (e.g. fixed deposits/ recurring deposits).
It not only keeps the deposit safe but also pays a small percent of interest on such deposit. An important point to note here is that banks pay depositors less interest than the interest they receive from their borrowers and this difference is the banks' main income.
Banks act as intermediaries between depositors (who deposit money with the bank) and borrowers (to borrow money from the bank). Banks also provide other financial services, such as currency exchange, wealth management, International services, online banking services, locker services and cross selling of third party products like insurance & mutual funds.
Banking operations are continually progressing with the help of deployment of newer and advanced technology which is resulting in an increase in revenue, minimising their costs, efficiently managing risk and establishing better customer relationships.
Why people keep their money in banks?
If you keep your money with a bank, it not only protects your money but offers you an interest based on tenure of deposits. This is the most important reason why people keep their money in a bank.
Interested to know Pledge Vs Hypothecation Vs Mortgage Vs Assignment
Role of Banks
There are multiple roles of banks, as mentioned below:
- A bank's most important role is matching up creditors and borrowers
- Transforming short term deposits into longer term lending
- Banks are essential to the domestic and international payments system
- Mobilising Savings for Capital Formation
- Financing Industrial Sector
- Banks play a vital role in economic development by removing the deficiency of capital by stimulating savings and investment
- Banks also create money
Types of Banks
Following are the types of banks and their functions:
- Retail/ Commercial Banks
- They provide banking services to general public.
- They manage savings, provide cheque books, credit and debit cards.
- They act as intermediary to pay bills through net banking and standing orders, providing cash withdrawal facilities.
- Investment Banks
- Investment banks offer financial services to other financial institutions and corporates.
- Their main activity is the issuance of securities for a listed company, either through an IPO or a secondary issue, in order to raise capital for expansion.
- They also provide investment advice to and broking on behalf of institutional investors and act as an intermediary for their clients engaged in mergers and acquisitions.
- Central Bank
- It is normally government owned Bank or banker to the government.
- It controls and monitors the banking and financial system of the country.
- It acts a regulator of the banking system in the country.
- It formulates, implements and monitors the monetary policy.
- Banking system cannot supply liquidity or control the cash interest rate in absense of a central bank.
- It has functions of controlling money supply in the system, monitoring different key indicators like GDP and inflation and also controlling foreign exchange in the country.
- It provides liquidity to the banking system and act as the lender of last resort in event of a crisis.
- India's central bank is the "Reserve Bank of India (RBI)". The RBI was established in 1935. It was nationalised in 1949.
- Co-operative Banks
- They are generally not-for-profit cooperatives owned by the depositors
- They are organized and managed on the principal of co-operation, self-help, and mutual help.
- They perform all the main banking activities such as deposit mobilization, extending loans and providing remittance facilities.
- They often offering more interest rates than that of for-profit banks as they do not pursue the goal of profit maximization.
- Post Office Savings Banks
- They are savings banks run by National Postal Department.
- They are one of the largest and oldest banking service institutions in any country.
- Postal savings systems provide a safe and convenient method to save money to those depositors who do not have access to banks.
- They act to promote savings among the poor.
- Offshore/ Foreign Banks
- They are located outside the country of residence of the depositor, typically in a low tax jurisdiction in order to provide financial and legal advantages.
- They are the Banks located at international places to enjoy relaxed regulations.
- They provide benefits for international business.
- Their functions also include maintaining privacy and asset protection.
What is Banking Ombudsman?
Banking Ombudsman is the senior official appointed by the RBI to redress the complaints related to and raised by bank customers. It is run by the RBI directly to ensure customer protection in the banking industry.
This is the service setup by RBI under the guidelines called "Banking Ombudsman Scheme, 2006" wherein your complaints against your bankers will be resolved with expeditious and inexpensive manner.
All public, private, RRBs and co-operative banks come under Banking Ombudsman. This is the free service provided by RBI.
As a banking customer, you can raise your complaints such as refusal to open deposit account, refusal to close or delay in closing accounts, levying charges without prior notice, non acceptance of your loan application, delay in loan processing, not adhering to fair practices, fraudulent transfer of amount by net banking, and so on.
Interested to know Bank Ombudsman Addresses
Important & Interesting Facts about Banks in India
- India has the highest number of bank branches in the world. According to IMF data for 2015 there are over 1.2 lakh bank branches in India, followed by China and Colombia with over 95,680 and 94,074 bank branches respectively
- India has 42.54 bank branches per 1,000 sq km, out of which nearly 34% are located in the rural areas
- Currently, 56 Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are operating in the country with total deposits of Rs 3,59,321 crore, advances of Rs 2,30,387 crore and 21,294 reporting offices as of June 2017, according to data from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- RBI was also the central bank for two other countries. It played the role of Central Bank of Pakistan till June 1948 and the Central Bank of Burma (Myanmar) till April 1947
- On 19 July 1969, the Indian government nationalised 14 major private banks and in 1980, 6 more private banks were nationalised
- RBI in 1993 gave licences to 12 Private banks in 2 phases; 10 private banks in 1993 and 2 private banks in 2003-2004
- State Bank of India (SBI) is one of the largest employers in India
- First Governor of RBI : Mr. Osborne Smith (1935-1937)
- First Indian Governor of RBI : Mr. C D Deshmukh (1943-1949)
- First Bank Set Up in India : Bank of Hindustan in 1770
- First Bank that is oldest Public Bank in India : Allahabad Bank
- First Indian bank to open branch outside India (in London in 1946): Bank of India
- First Regional Rural Bank Name: Prathama Grameen Bank
- First Bank to Introduce Cheque System in India : Bengal Bank 1784
- First Bank to introduce Internet Banking : ICICI BANK
- First Bank to introduce Mutual Fund : State Bank of India
- First Bank to introduce Credit Card in India : Central Bank of India
- First Foreign Bank in India : Comptoire d'Escompte de Paris of France in 1860
- The bank which was inaugurated by Mahatma Gandhi in 1919: Union Bank of India
- The bank which was conceived by Shri GD Birla: Uco Bank
- Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC) introduced first time ATM in India in 1987, Mumbai
- India has the largest postal network in the world. There were 1,54,939 post offices in India of which 1,39,222 (almost 90 %) are in rural areas
- Post Office Saving Bank (POSB) had a customer base of 33.03 crore as on March 31, 2015
Conslusion
I hope I have been able to explain about Banking, Banks and other related items to the Banking Industry in my above blog.
 Anupama is a Co-Founder of CodeForBanks.com. She is an MBA (Finance) and Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA). She also carries a Fellowship degree in Life Insurance Sector and is a Master of Computer Application (MCA). She is an expert in Finance Field with an experience of over 18 years on different managerial positions in finance industry including Stock Market, Depository and Mutual Fund Sectors. Apart from that she has remained for few years in the field of marketing as well. Her suggestions and advice for investments have been very useful to many people.
Anupama is a Co-Founder of CodeForBanks.com. She is an MBA (Finance) and Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA). She also carries a Fellowship degree in Life Insurance Sector and is a Master of Computer Application (MCA). She is an expert in Finance Field with an experience of over 18 years on different managerial positions in finance industry including Stock Market, Depository and Mutual Fund Sectors. Apart from that she has remained for few years in the field of marketing as well. Her suggestions and advice for investments have been very useful to many people.Her vast interest & expertise in the field of finance have encouraged her to write the articles so that others can also get benefitted out of them. She never loses any opportunity to learn and be creative. She is a valuable asset for CodeForBanks.com & important resource to all those around her.
Popular Posts
-
Telangana Grameena Bank MSE Loans
26 Mar 2024
-
Saptagiri Grameena Bank Variable Recurring Deposit
26 Mar 2024
-
All About Chaitanya Godavari Grameena Bank Mobile App CGGB Money 2.0
26 Mar 2024
-
Saptagiri Grameena Bank Plot Loan Scheme
26 Mar 2024
-
CGGB Recurring Plus: A Tool for Weath Creation
26 Mar 2024
-
Earn Up to 8.60% Under Chaitanya Godavari Grameena Bank Kalpalatha Term Deposit
26 Mar 2024
-
Special Deposit Schemes Offered by Andhra Pragathi Grameena Bank
20 Mar 2024
-
All About Baroda UP Bank Mobile App BUPB M-Tarang
20 Mar 2024
-
Secure Health Cover and High Returns: Invest in HDFC Bank FD
01 Jan 2024
-
Benefit from the Merger of IDFC Financial Holding Co and IDFC First Bank
01 Jan 2024


